Acids: taste sour and feel sticky; pH 0-6.9; turns litmus paper red
Bases: taste bitter and feel slippery; pH 8-14; turns litmus paper blue
Arrhenius Acids and Bases
acids: produce H+ ions in solution
bases: produce OH- ions in solution
Bronsted Lowery Acids and Bases
acids: produce/donate the H+ ion (proton) in the reaction
bases: accept the H+ ion (proton) in the reaction
conjugate base: produced by acids when they lose a proton
conjugate acid: produced by bases when they gain a proton
Acid Strength
- strong acids:ions completely disassociate in an aqueous solution
- examples of strong acids: HClO4, HClO3, HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4
- largest Ka value is the strongest acid
Strength of Salt
- Strong Acid + Strong Base = Neutral Salt
- Strong Acid + Weak Base = Acidic Salt
- Weak Acid + Strong Base = Basic Salt
- Weak Acid + Weak Base = Neutral Salt
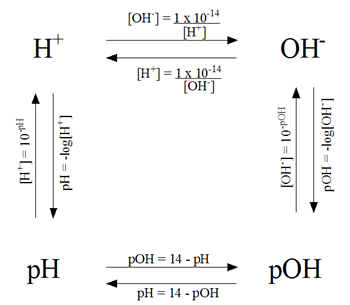
Ion Product of Water
- the ion produce of water is always 1.0*10^-14 at 25 degrees Celsius
- in an acidic solution, the H+>OH-
- in a basic solution, the H+<OH-
- in a neutral solution H+=OH-
Solving for pH and pOH for strong acids
Solving for pH of weak acid
Links
this link helps with ICE box problems:
practice for finding pH
help with Bronsted Lowery problems
Key Terms Quizlet
this link helps with ICE box problems:
practice for finding pH
help with Bronsted Lowery problems
Key Terms Quizlet

This whole post in general really helped me to clear up any slight confusions I had before taking the test. Although I did run into some slight problems I remembered most of it due to your quick summary!
ReplyDeleteThis notes summary is really awesome! I love how you color coded your acids and bases rules; it was a great way to remember them!
ReplyDelete